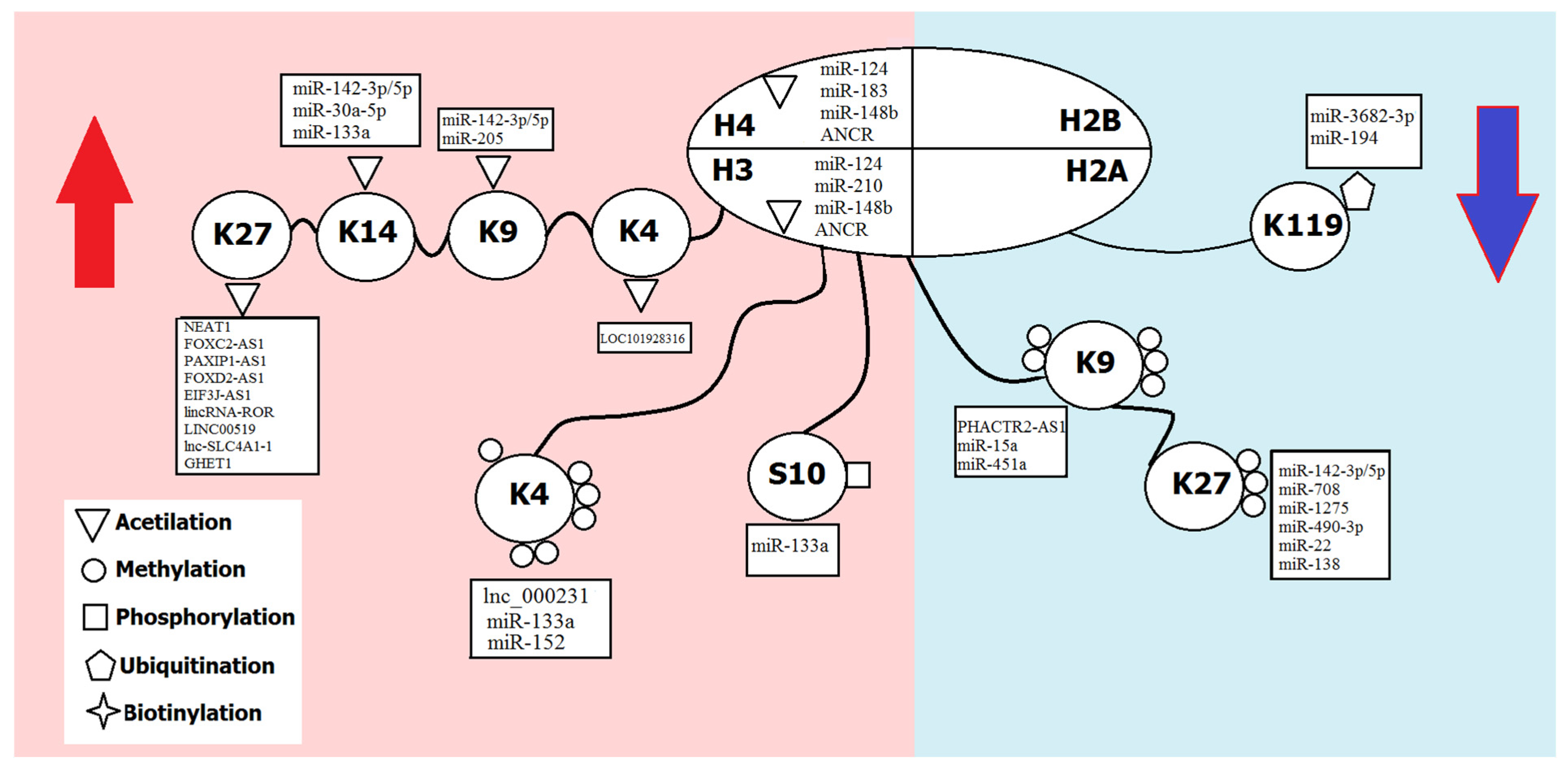
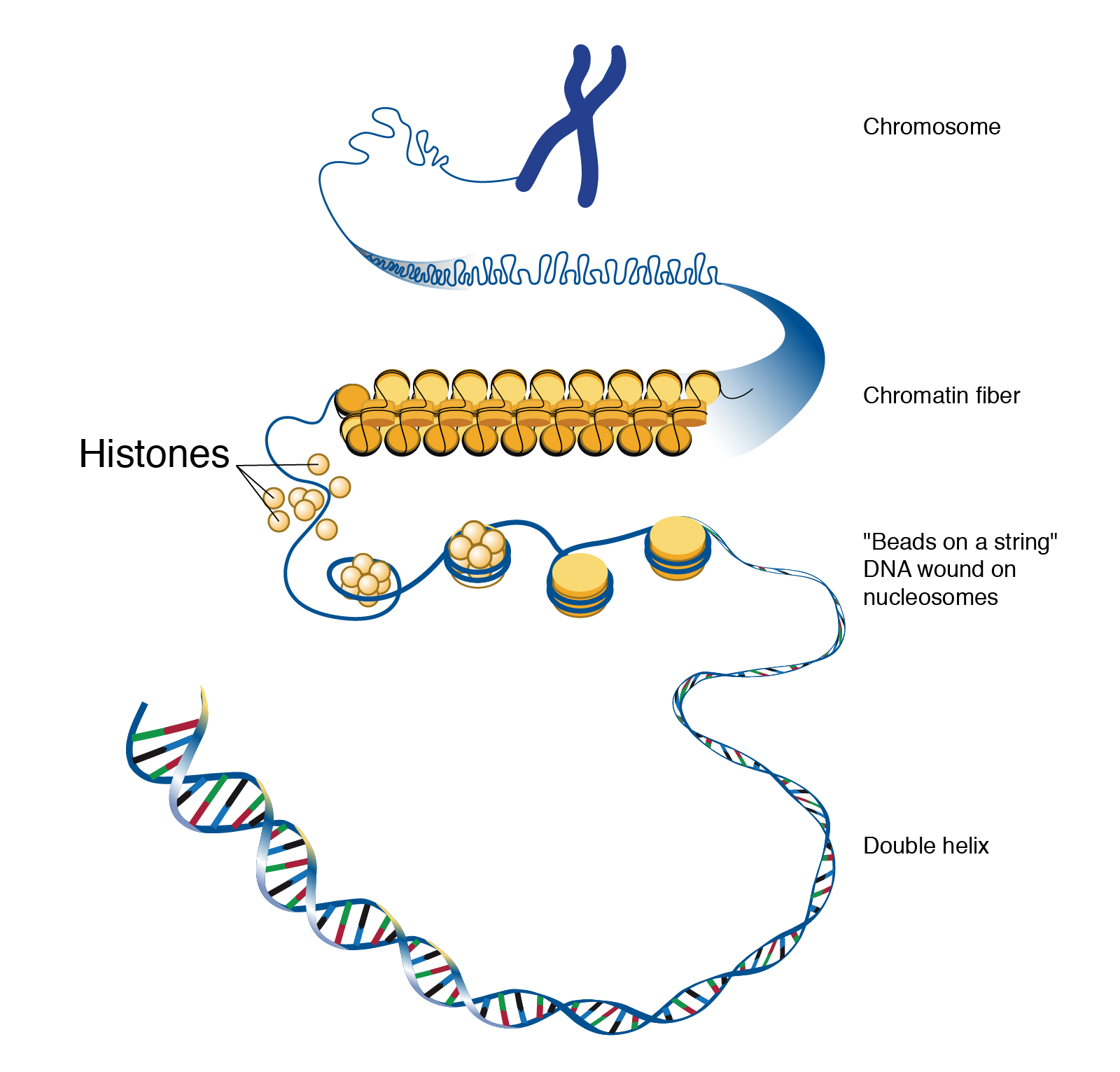
Parenta Care Distance Of Histones Chart
Parenta Care Distance Of Histones Chart - 5 and 6), we propose an alternative molecular mechanism, in which differential levels of accessible free histones are used to prevent local histone recycling in euchromatin but promote it in. Web recent data have identified histone chaperone activities that are intrinsic components of the replisome and implicate them in maintaining parental histones during dna replication. Web our data suggest that parental histones harboring ptms are recycled, and their genomic positions are restored during dna replication to preserve the epigenetic landscape. We review the evidence suggesting that such effects are mediated by epigenetic mechanisms, including dna methylation and hydroxymethylation across gr promoter regions. Web we reveal the importance of parental histone recycling in the efficiency of ssdna gap filling by hr during ddt, as determined by the analyses of mutants specifically affected in the deposition of parental histones at the lagging or leading strand. We summarize this work and use it to propose a model for how the fate of parental histones is controlled. Web parental histones, which are inherited from parental strands, are recycled and deposited onto replicating dna strands, while newly synthesized histones are recruited de novo and deposited to restore histone levels. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. Web described the inheritance patterns of parental histones on the genome. 5 and 6), we propose an alternative molecular mechanism, in which differential levels of accessible free histones are used to prevent local histone recycling in euchromatin but promote it in. Web recent data have identified histone chaperone activities that are intrinsic components of the replisome and implicate them in maintaining parental histones during dna replication. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. We summarize this work and use it to propose a model for how the fate of parental histones is controlled. Web we reveal the importance of parental histone recycling in the efficiency of ssdna gap filling by hr during ddt, as determined by the analyses of mutants specifically affected in the deposition of parental histones at the lagging or leading strand. Web parental histones, which are inherited from parental strands, are recycled and deposited onto replicating dna strands, while newly synthesized histones are recruited de novo and deposited to restore histone levels. Web on the basis of our findings that the efficiency of parental histone recycling depends on the concentration of newly synthesized histones (figs. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. Web described the inheritance patterns of parental histones on the genome. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. Web parental histones, which are inherited from parental strands, are recycled and deposited onto replicating dna strands, while newly synthesized histones are recruited de novo and deposited to restore histone levels. Web recent data have identified histone chaperone activities that are intrinsic components of the replisome and implicate them. Web these results underscore the importance of both symmetric distribution of parental histones and their density at daughter strands for epigenetic inheritance and unveil distinctive properties of parental histone chaperones during dna replication. Web recent data have identified histone chaperone activities that are intrinsic components of the replisome and implicate them in maintaining parental histones during dna replication. Web modified. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. Web our data suggest that parental histones harboring ptms are recycled, and their genomic positions are restored during dna replication to preserve the epigenetic landscape. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. We review the evidence suggesting. Web our data suggest that parental histones harboring ptms are recycled, and their genomic positions are restored during dna replication to preserve the epigenetic landscape. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. A binary choice may be made for each (h3/h4) 2 between recycling through a soluble pool and redeposition with positional memory. Web these results. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. We summarize this work and use it to propose a model for how the fate of parental histones is controlled. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. Web in humans, childhood maltreatment associates decreased hippocampal gr expression and increased stress responses in adulthood. Web these results underscore the importance of both symmetric distribution of parental histones and their density at daughter strands for epigenetic inheritance and unveil distinctive. We summarize this work and use it to propose a model for how the fate of parental histones is controlled. Web in humans, childhood maltreatment associates decreased hippocampal gr expression and increased stress responses in adulthood. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. Web these results underscore the importance of both symmetric distribution of parental histones. Web in work published in december 2020 in the journal plos biology, the team showed that this histone, a short variant normally found only in the developing sperm and egg cells of placental mammals, supports proper development of embryos formed from those sperm and eggs. Web we reveal the importance of parental histone recycling in the efficiency of ssdna gap. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. Web described the inheritance patterns of parental histones on the genome. Web parental histones can be inherited close to their starting dna sequence (i.e., with positional memory). Web we reveal the importance of parental histone recycling in the efficiency of ssdna. Web our data suggest that parental histones harboring ptms are recycled, and their genomic positions are restored during dna replication to preserve the epigenetic landscape. We review the evidence suggesting that such effects are mediated by epigenetic mechanisms, including dna methylation and hydroxymethylation across gr promoter regions. Web recent data have identified histone chaperone activities that are intrinsic components of. Web these results underscore the importance of both symmetric distribution of parental histones and their density at daughter strands for epigenetic inheritance and unveil distinctive properties of parental histone chaperones during dna replication. We demonstrate that symmetric parental histone deposition to sister chromatids contributes to cellular differentiation and development. 5 and 6), we propose an alternative molecular mechanism, in which differential levels of accessible free histones are used to prevent local histone recycling in euchromatin but promote it in. Web parental histones, which are inherited from parental strands, are recycled and deposited onto replicating dna strands, while newly synthesized histones are recruited de novo and deposited to restore histone levels. Histone chaperone activities intrinsic to the replisome may mediate positional memory. Web modified parental histones are segregated symmetrically to daughter dna strands during replication and can be inherited through mitosis. How this may sustain the epigenome and cell identity remains unknown. Web in humans, childhood maltreatment associates decreased hippocampal gr expression and increased stress responses in adulthood. Web recent data have identified histone chaperone activities that are intrinsic components of the replisome and implicate them in maintaining parental histones during dna replication. Web on the basis of our findings that the efficiency of parental histone recycling depends on the concentration of newly synthesized histones (figs. Web we reveal the importance of parental histone recycling in the efficiency of ssdna gap filling by hr during ddt, as determined by the analyses of mutants specifically affected in the deposition of parental histones at the lagging or leading strand. Web parental histones can be inherited close to their starting dna sequence (i.e., with positional memory). Web our results demonstrate that disrupting accurate allocation of parental histones during cell differentiation leads to impaired neural differentiation, providing direct evidence that proper. Web our data suggest that parental histones harboring ptms are recycled, and their genomic positions are restored during dna replication to preserve the epigenetic landscape. A binary choice may be made for each (h3/h4) 2 between recycling through a soluble pool and redeposition with positional memory. We review the evidence suggesting that such effects are mediated by epigenetic mechanisms, including dna methylation and hydroxymethylation across gr promoter regions.IJMS Free FullText Histone Modifications and NonCoding RNAs
Histone
CTCFL Interacts with Histones H1, H2A, and H3 (A) Farwestern analysis
RealTime Tracking of Parental Histones Reveals Their Contribution to
Plotting parental heights on distance charts and determining adult
Eviction and shielding of DNAbound histones mediated by histone
Interactions of regulatory residues from the histone tails
—Telomere distance plots of genome expression data for the (A) histone
The 3 ′ ends of the fulllength histone mRNAs are not affected by
resetting in the human germ line entails histone
Web Described The Inheritance Patterns Of Parental Histones On The Genome.
We Summarize This Work And Use It To Propose A Model For How The Fate Of Parental Histones Is Controlled.
Web Modified Parental Histones Are Segregated Symmetrically To Daughter Dna Strands During Replication And Can Be Inherited Through Mitosis.
Web In Work Published In December 2020 In The Journal Plos Biology, The Team Showed That This Histone, A Short Variant Normally Found Only In The Developing Sperm And Egg Cells Of Placental Mammals, Supports Proper Development Of Embryos Formed From Those Sperm And Eggs.
Related Post: