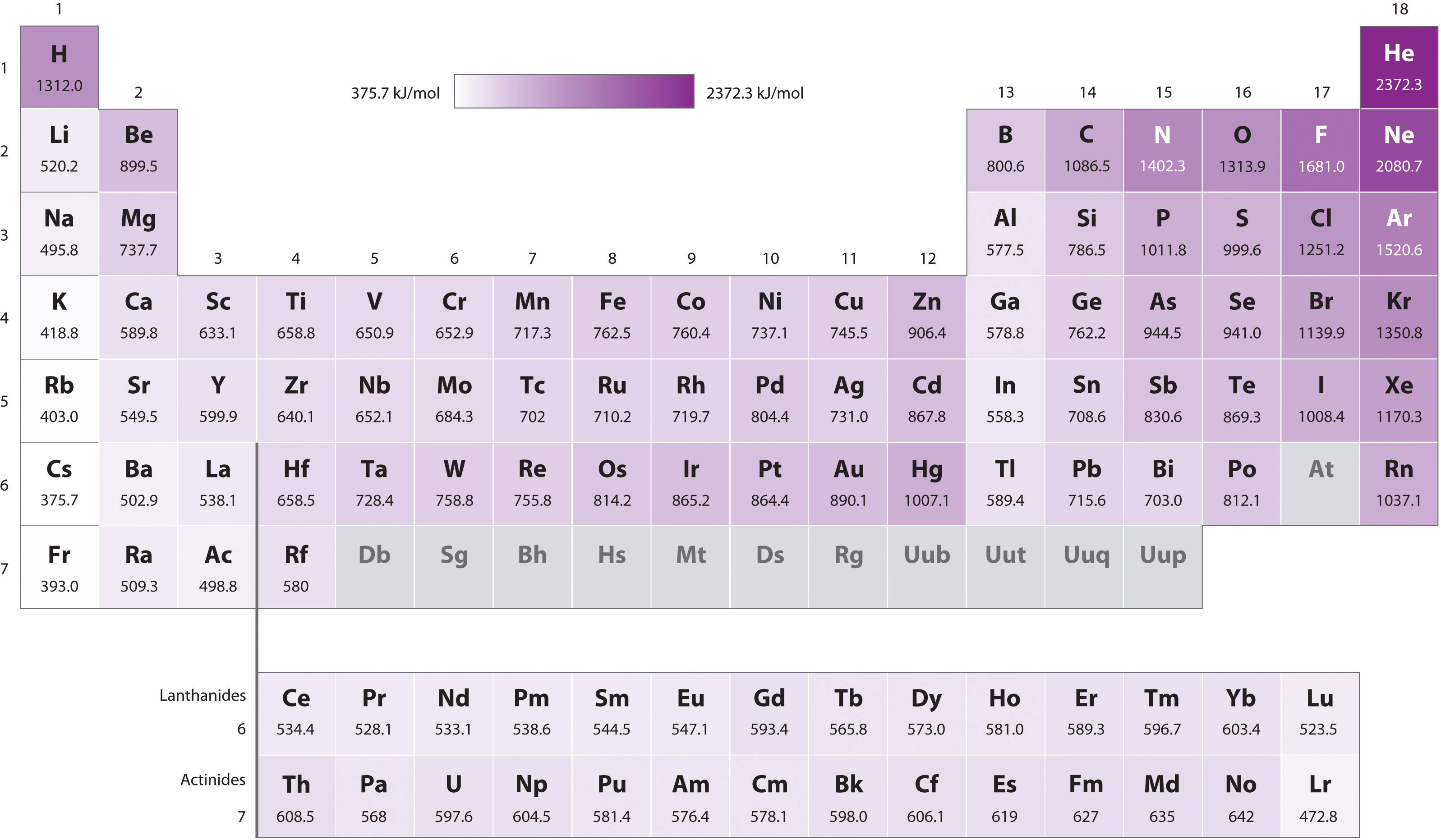
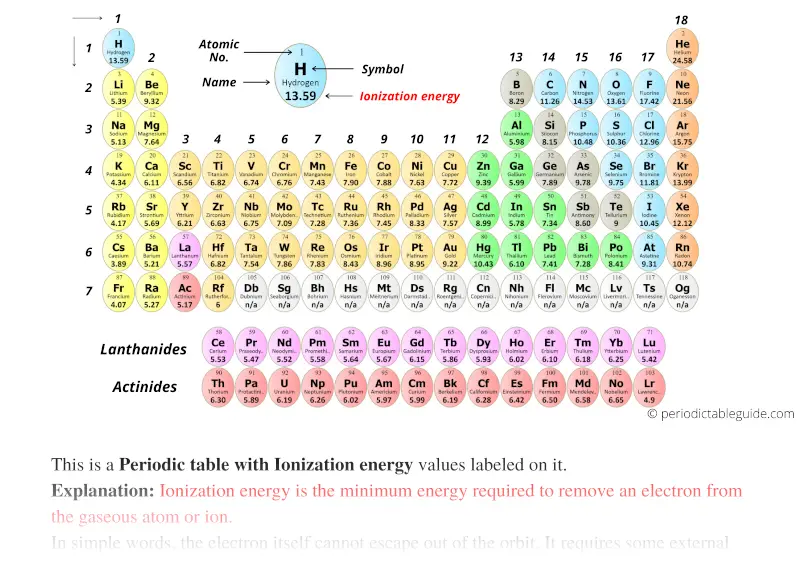
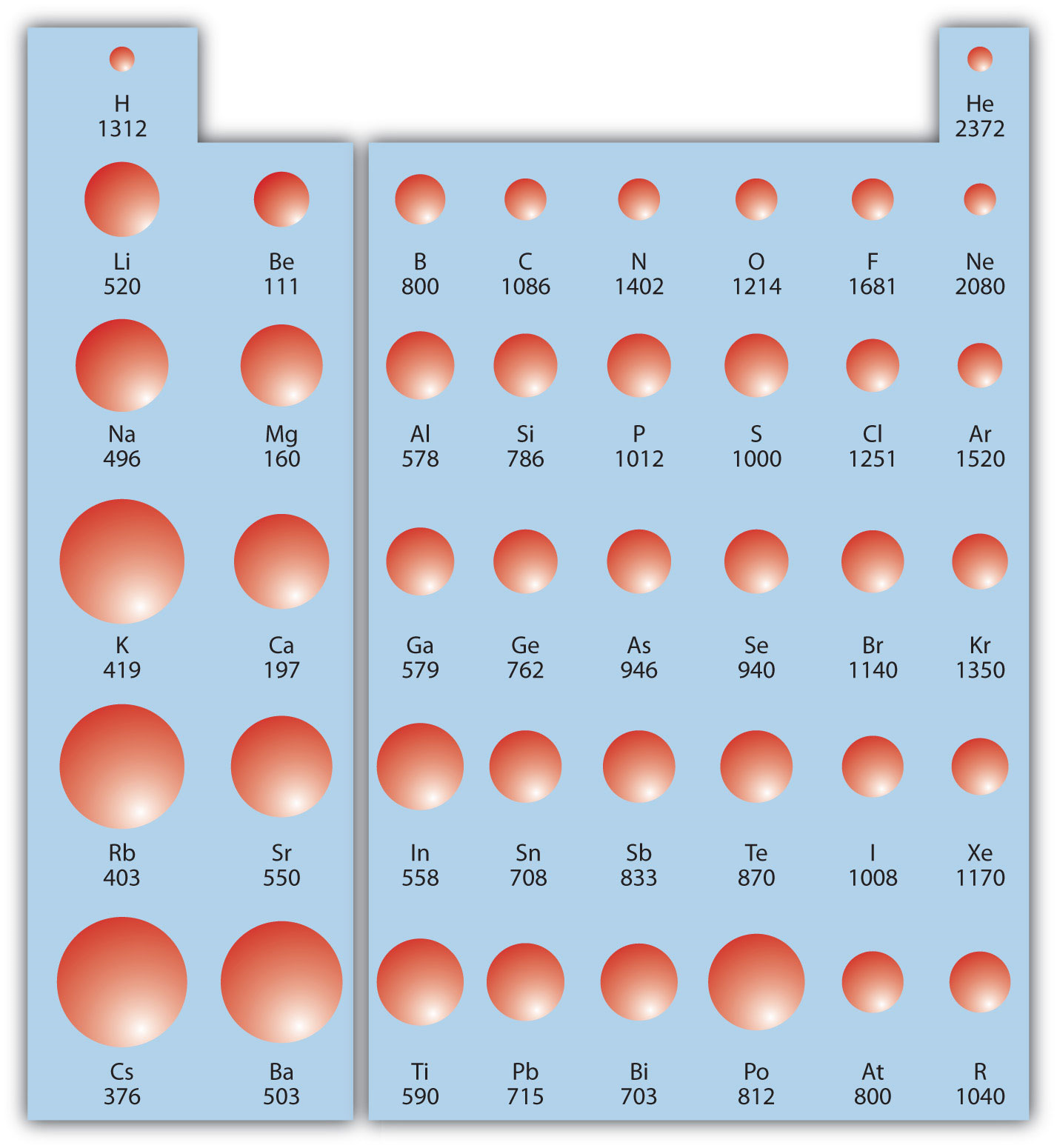
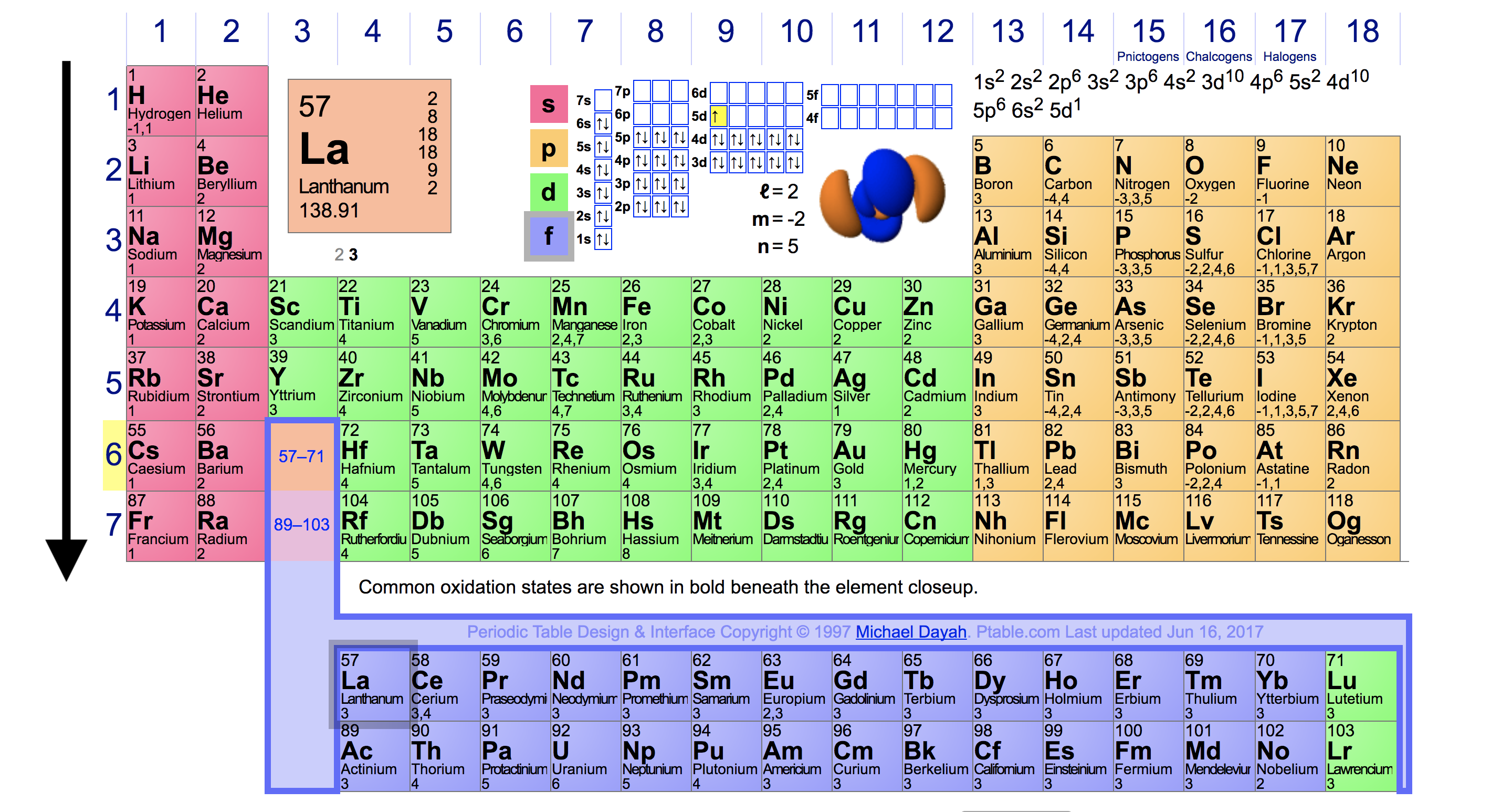
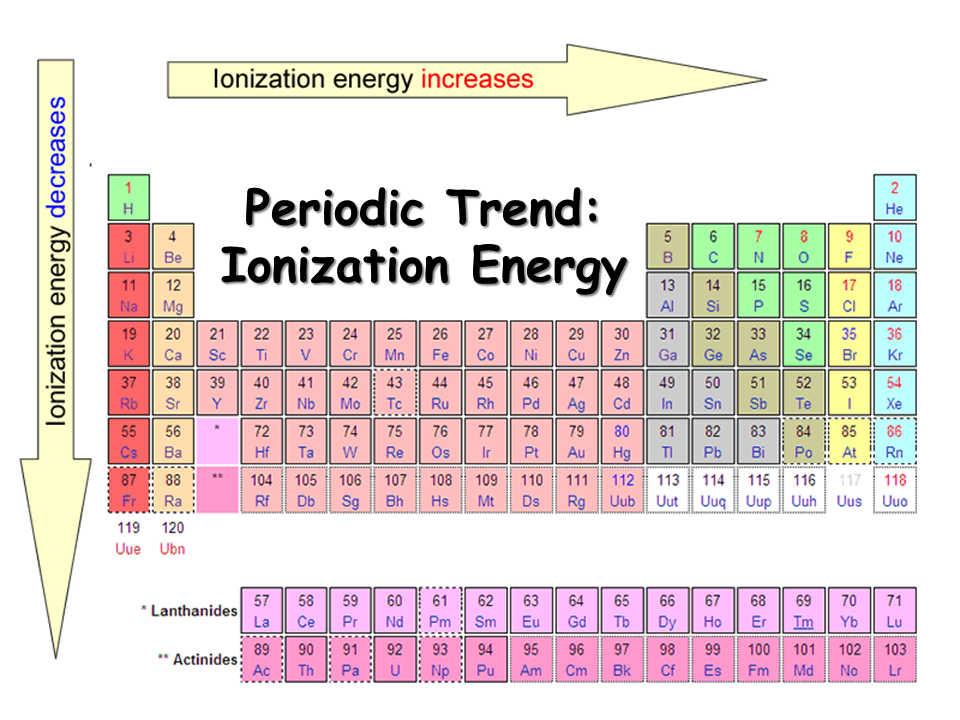
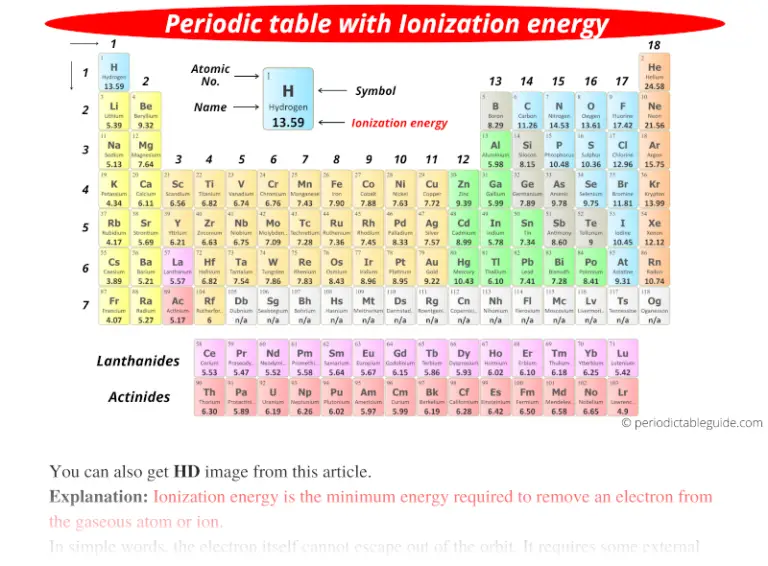
Ionization Energy Chart
Ionization Energy Chart - The measurement is performed in the gas phase on single atoms. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. Web the periodic table of the elements (with ionization energies) 1. 1 ev / atom = 96.49 kj / mol. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. It measures the capability of an atom to lose an electron during a chemical reaction. Web ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove a loosely bound electron of an atom or molecule in the gaseous state. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of light quanta or electrons accelerated to a known energy that will kick out the least bound atomic electrons. Alkali metals alkaline earth metals. Web ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove a loosely bound electron of an atom or molecule in the gaseous state. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): 1 ev / atom = 96.49 kj / mol. Alkali metals alkaline earth metals. Ionization energy is always positive. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. The measurement is performed in the gas phase on single atoms. If an atom possesses more than one electron, the amount of energy needed to remove successive electrons increases steadily. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove a loosely bound electron of an atom or molecule in the. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of light quanta or electrons accelerated to a known energy that will kick out the least bound atomic electrons. 1 ev / atom = 96.49 kj / mol. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in. The measurement is performed in the gas phase on single atoms. These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. 1 ev / atom = 96.49 kj / mol. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of light quanta or electrons accelerated to a known energy that will kick out the least bound atomic electrons. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. These tables list values of molar. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. Web typical units. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. 1 ev / atom = 96.49 kj / mol. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. The measurement is performed in the gas phase on single atoms. Web molar ionization energies of the elements. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): The measurement. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. Alkali metals alkaline earth metals. Web ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove a loosely bound electron of an atom or molecule in the gaseous state. First ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization. The measurement is performed in the gas phase on single atoms. It measures the capability of an atom to lose an electron during a chemical reaction. Web molar ionization energies of the elements. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. If an atom possesses more than one electron,. These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Ionization energy is always positive. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. Web molar ionization energies of the elements. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of light quanta or. Web the periodic table of the elements (with ionization energies) 1. These tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. The ionization energy of the elements within a period. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. 1 ev / atom = 96.49 kj / mol. Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web the ionization energy of atoms, denoted e i, is measured by finding the minimal energy of light quanta or electrons accelerated to a known energy that will kick out the least bound atomic electrons. If an atom possesses more than one electron, the amount of energy needed to remove successive electrons increases steadily. Web typical units for ionization energies are kilojoules/mole (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev): The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Web ionization energy chart of all the elements is given below. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. Web ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. It measures the capability of an atom to lose an electron during a chemical reaction. Web ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove a loosely bound electron of an atom or molecule in the gaseous state. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions.6.4 Ionization Energy Chemistry LibreTexts
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy CK12 Foundation
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
9.9 Periodic Trends Atomic Size, Ionization Energy, and Metallic
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy Chemistry Socratic
What Is Ionization Energy? Definition and Trend
Ionization Enthalpy NEET Lab
Among the Following Which Element Has the Lowest Ionization Energy
The Parts of the Periodic Table
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)
Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals.
Web Molar Ionization Energies Of The Elements.
The Measurement Is Performed In The Gas Phase On Single Atoms.
First Ionization Energy, Second Ionization Energy As Well As Third Ionization Energy Of The Elements Are Given In This Chart.
Related Post: