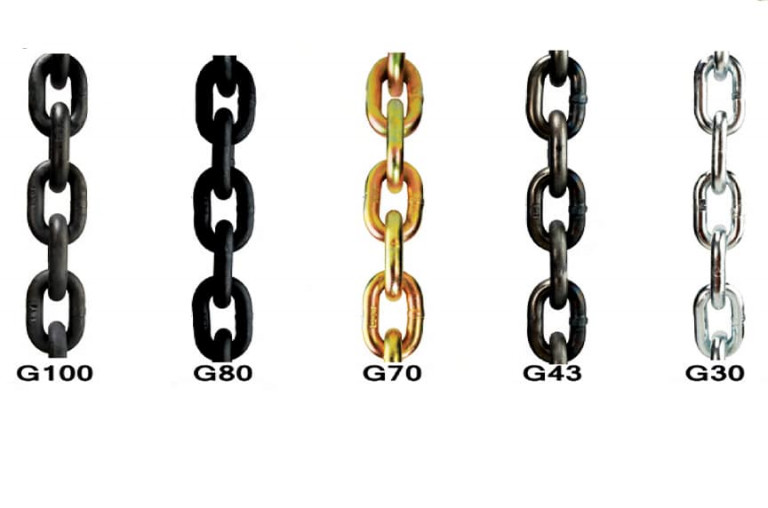
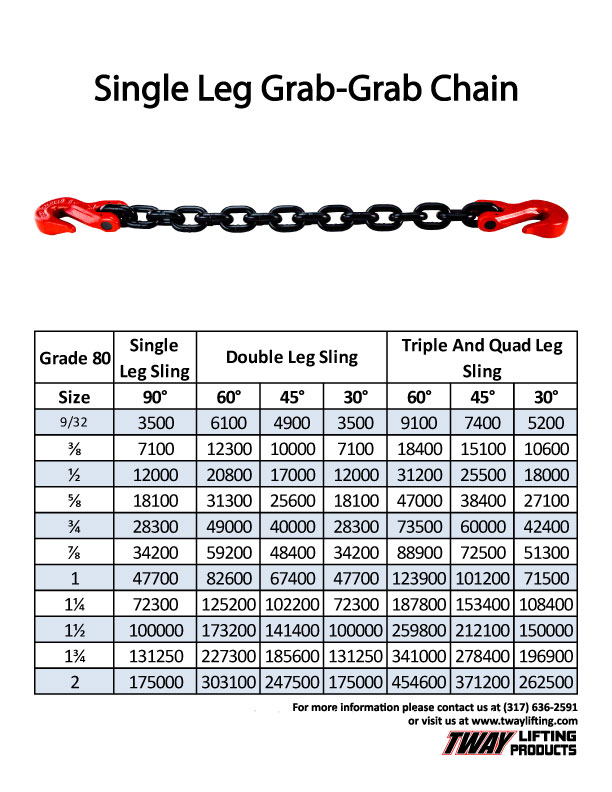
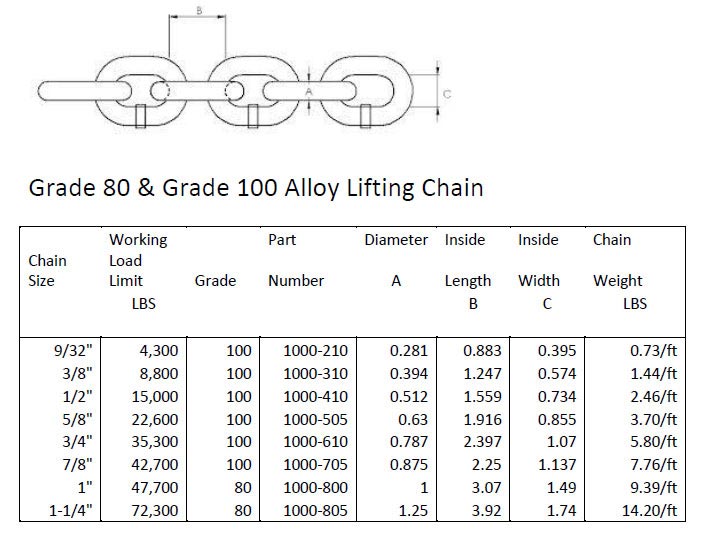
Chain Grade Chart
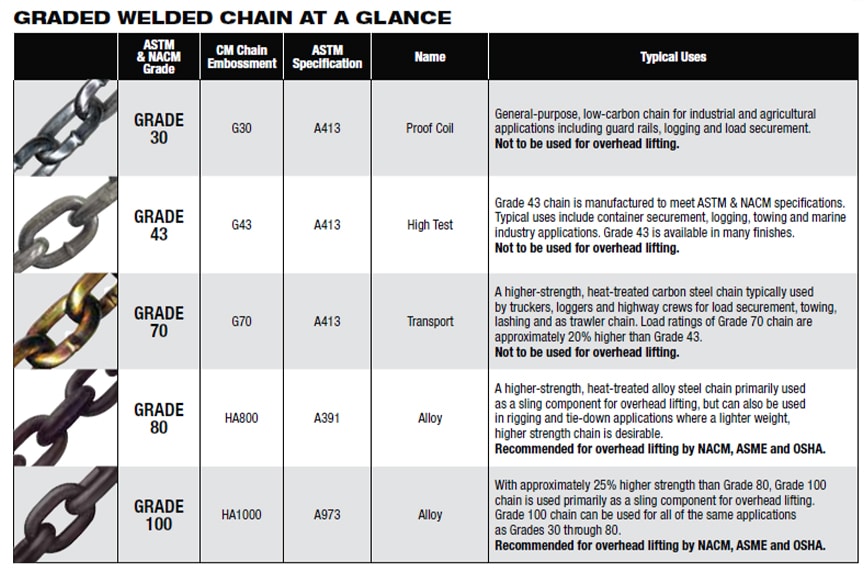
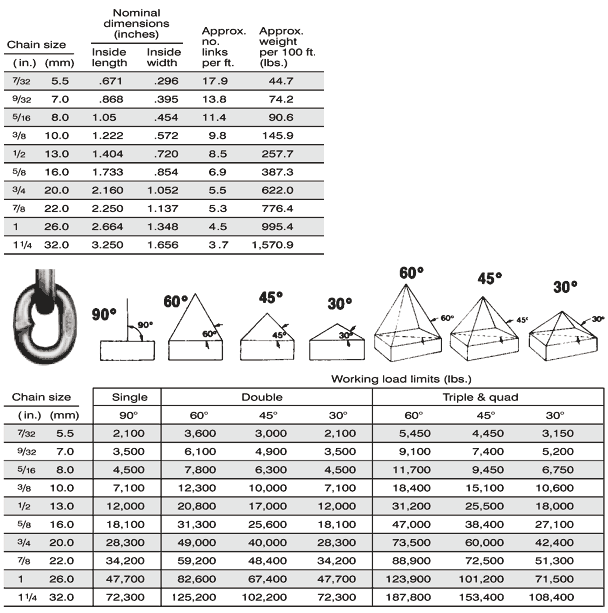
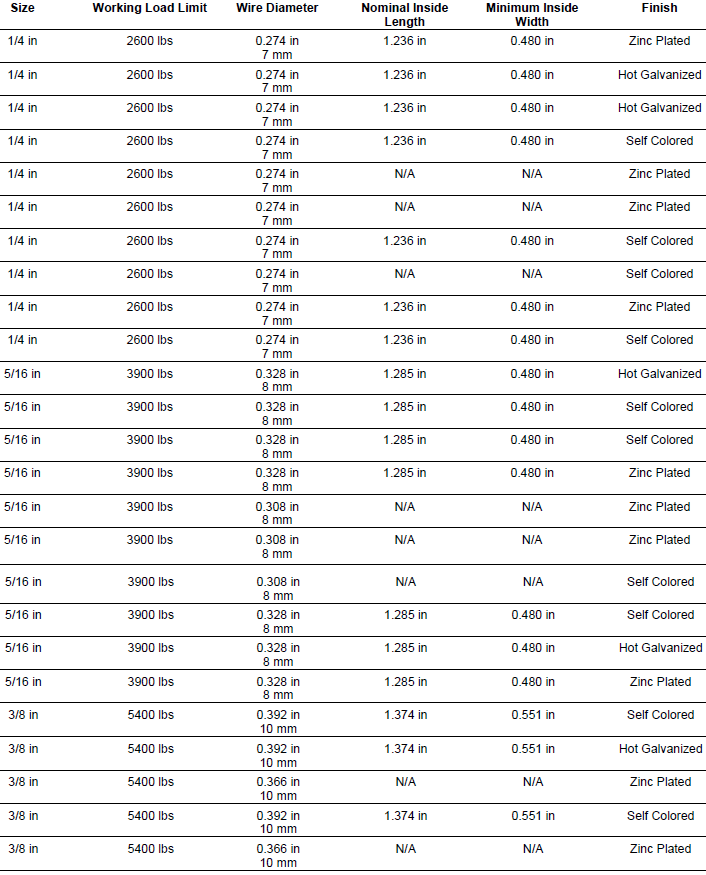
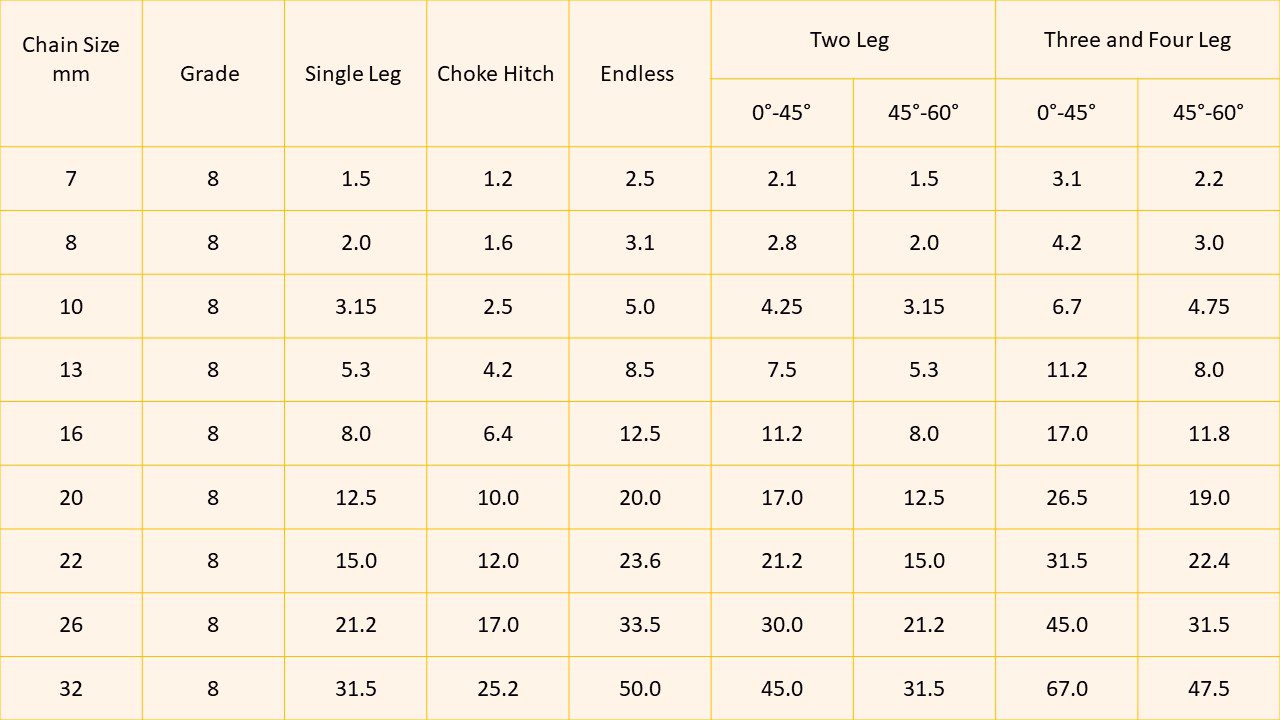
Chain Grade Chart - Web which chain grade should be used for which type of application? Grades help determine what sort of applications are appropriate for a given chain. Web chain grades are a standard method for showing the ultimate breaking strength (tensile strength) of a chain. Alloy chain grade 80 or grade 100 should be used for overhead lifting. Web the different chain grades explained, with their permitted uses and free charts/cheats to download and print. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. G30, g43, g70, g80, and g100. Web chains come in various grades, each denoting specific characteristics and applications. Web in the intricate world of industrial chains, understanding the grading system is paramount. Web this guide will delve into the various chain grades used in the rigging industry, their common applications, differences, potential problems, and common misuse scenarios. Web the biggest difference between grades of chain is that carbon steel chain—grade 30, 43, and 70—is not recommended for overhead lifting, while alloy steel chain—grade 80, 100, and 120—is recommended for use in sling assemblies and overhead lifting applications. Web chain grades are a standard method for showing the ultimate breaking strength (tensile strength) of a chain. Web in this article, we unravel the intricacies of identifying chain grade, shedding light on the key factors, markings, and insights that empower industries to distinguish between different chain grades accurately. Grades wise chain usage and safety standards. Web which chain grade should be used for which type of application? Alloy chain grade 80 or grade 100 should be used for overhead lifting. Web this guide will delve into the various chain grades used in the rigging industry, their common applications, differences, potential problems, and common misuse scenarios. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. Web complete flatbedder’s guide on cargo chain grades, grade types and chain strength with chart. Common grades include grade 30, grade 43, grade 70, grade 80, and grade 100, each tailored for distinct use cases. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. Astm states that alloy chain shall be able to elongate a minimum of 20% before fracture (7.3.5). Grades help determine what sort of applications are appropriate for a given chain. Web which chain grade should be used for which type of application? Grades wise. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. Grades help determine what sort of applications are appropriate for a given chain. G30, g43, g70, g80, and g100. Web the biggest difference between grades of chain is that carbon steel chain—grade 30, 43, and 70—is not recommended for overhead lifting, while alloy steel. Grades wise chain usage and safety standards. Common grades include grade 30, grade 43, grade 70, grade 80, and grade 100, each tailored for distinct use cases. Web the biggest difference between grades of chain is that carbon steel chain—grade 30, 43, and 70—is not recommended for overhead lifting, while alloy steel chain—grade 80, 100, and 120—is recommended for use. Grades wise chain usage and safety standards. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. Web the different chain grades explained, with their permitted uses and free charts/cheats to download and print. Web chains come in various grades, each denoting specific characteristics and applications. G30, g43, g70, g80, and g100. This article embarks on a journey through the ratings of chain grades, deciphering the significance behind the numbers and letters that define strength, durability, and performance. Web chain grades are a standard method for showing the ultimate breaking strength (tensile strength) of a chain. Web the different chain grades explained, with their permitted uses and free charts/cheats to download and. Web which chain grade should be used for which type of application? Web complete flatbedder’s guide on cargo chain grades, grade types and chain strength with chart. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. Grades wise chain usage and safety standards. This article embarks on a journey through the ratings of. Web complete flatbedder’s guide on cargo chain grades, grade types and chain strength with chart. Web chains come in various grades, each denoting specific characteristics and applications. Web chain grades are a standard method for showing the ultimate breaking strength (tensile strength) of a chain. Web in the intricate world of industrial chains, understanding the grading system is paramount. Common. Web chains come in various grades, each denoting specific characteristics and applications. Common grades include grade 30, grade 43, grade 70, grade 80, and grade 100, each tailored for distinct use cases. G30, g43, g70, g80, and g100. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. Web the biggest difference between grades. Astm states that alloy chain shall be able to elongate a minimum of 20% before fracture (7.3.5). This article embarks on a journey through the ratings of chain grades, deciphering the significance behind the numbers and letters that define strength, durability, and performance. Web in this article, we unravel the intricacies of identifying chain grade, shedding light on the key. Web which chain grade should be used for which type of application? Astm states that alloy chain shall be able to elongate a minimum of 20% before fracture (7.3.5). Web in the intricate world of industrial chains, understanding the grading system is paramount. Web the different chain grades explained, with their permitted uses and free charts/cheats to download and print.. Web which chain grade should be used for which type of application? Web the different chain grades explained, with their permitted uses and free charts/cheats to download and print. Web this guide will delve into the various chain grades used in the rigging industry, their common applications, differences, potential problems, and common misuse scenarios. G30, g43, g70, g80, and g100. Astm states that alloy chain shall be able to elongate a minimum of 20% before fracture (7.3.5). Web complete flatbedder’s guide on cargo chain grades, grade types and chain strength with chart. This article embarks on a journey through the ratings of chain grades, deciphering the significance behind the numbers and letters that define strength, durability, and performance. Web chain grades are a standard method for showing the ultimate breaking strength (tensile strength) of a chain. Chain grades are determined by calculating newtons per square millimeter, using the formula “n/mm 2 ”. Web there are five grades of chain: Common grades include grade 30, grade 43, grade 70, grade 80, and grade 100, each tailored for distinct use cases. Web in this article, we unravel the intricacies of identifying chain grade, shedding light on the key factors, markings, and insights that empower industries to distinguish between different chain grades accurately. Web in the intricate world of industrial chains, understanding the grading system is paramount. Learn how to identify grades and marking of transport chains. Alloy chain grade 80 or grade 100 should be used for overhead lifting.What Are the Different Grades of Chain?
Chain Grades And Strengths Chart
Chain Grade Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Helpful Links Catena Inspection & Engineering Services
Chain Grades Chart Cargo Chain Strength and Grades Guide for Flatbedder’s
Chain Grades Chart Cargo Chain Strength And Grades Guide, 50 OFF
What Are the Different Grades of Chain?
Chain Grades Chart Cargo Chain Strength and Grades Guide for Flatbedder’s
Chain Grade Rating Chart Ponasa
Comparing Chain Grades U.S. Cargo Control US Cargo Control
Web The Biggest Difference Between Grades Of Chain Is That Carbon Steel Chain—Grade 30, 43, And 70—Is Not Recommended For Overhead Lifting, While Alloy Steel Chain—Grade 80, 100, And 120—Is Recommended For Use In Sling Assemblies And Overhead Lifting Applications.
Web Chains Come In Various Grades, Each Denoting Specific Characteristics And Applications.
Grades Wise Chain Usage And Safety Standards.
Grades Help Determine What Sort Of Applications Are Appropriate For A Given Chain.
Related Post: